Overview
The Seasonal adjustment Census X-13 analysis removes seasonal patterns, such as weather fluctuations or holiday effects, from time series. It’s useful when you want to analyze any data affected by seasonality.
Method
This analysis uses the X-13-ARIMA-SEATS program from the US Census Bureau, which is the most common method used around the world. A documentation regarding the full X-13 ARIMA-SEATS Seasonal Adjustment Program can be found here.
At the beginning Census invented a method and program that they have called "X-11". Then they have added extra steps like ARIMA or Easter effect which, when active, transform method into X-12 and after a few other addition into X-13-ARIMA-SEATS. In short, X-13 we use is X-11 base with additional settings you see in the analysis.
Limitations
We offer configuration of the most common settings from X-13-ARIMA-SEATS program.
Additionally, the input series must meet the following requirements:
- The series cannot be daily, weekly, or annual.
- There must be no missing values in the series (you can fill in missing values by using one of the methods in the conversion settings tab of the series list analysis).
- There must be no skipped dates in the series (you can make sure that all dates are included in the series by selecting all points from the observations drop-down menu in the series list).
- There are also limitations in the X-13-ARIMA-SEATS program when it comes to the maximum number of observations, maximum number of years etc..
Settings
See here pre-1.28 version view
Method
You can select from the following methods:
- X-11 - method from the Census Bureau program
- SEATS - program developed by the Bank of Spain
- Auto (X-11/SEATS) - for some series it is hard to find working settings in X-11/SEATS method. This one provides automated selection based on series' metadata. Additional columns which are controlled by this setting are disabled.
Type
Select whether your input series is a stock or flow series.
If Auto is selected, the class property of the time series is used to determine if it is a stock or a flow.
If you select Stock, the instruction type=stock will be added to the series element of the configuration passed to the X-13 ARIMA-SEATS program.
Holiday regressor
An option for selecting certain holidays as a regression variable in the X-13 Seasonal adjustment analysis. This works only for monthly data.
Chinese New Year
The Chinese New Year Holiday regressor utilizes a standard approach to account for the moving holiday effects from the Lunar holiday observed in some high-frequency time series data. While no universally agreed method exists, the literature thus far suggests an approach similar to what is being used in the application. Three regressors (in the form of dummy variables) are assigned to each of three sub-period windows of 20 days before, 7 days during, and 20 days after the holiday, capturing the differential effects on data from the lunar holiday.
Brazilian Carnival
The Brazilian Carnival holiday regressor utilizes a standard approach to account for the moving holiday effects from the holiday observed in some high-frequency time series data. While no universally agreed method exists, the literature thus far suggests an approach similar to what is being used in the application. Three regressors (in the form of dummy variables) are assigned to each of three sub-period windows of 3 days before, 6 days during, and 1 day after the Carnival, capturing the differential effects on data from the holiday.
Historical dates for the Brazilian Carnival were calculated using the dates of Easter sourced from U.S. Census Bureau using following formula:
- Beginning = Friday before Ash Wednesday, 51 days to Easter
- End = Ash Wednesday, 46 days to Easter
Brazilian Carnival was suspended in 1912 (following the death of the Baron of Rio Branco) and in 2021 (due to COVID-19 Pandemic). In 2022, the Carnival was held on 20-30 April.
For further insights into the theoretical and practical considerations on seasonal adjustment and moving holiday adjustments, please click here.
ARIMA
Selecting this option instructs the program to use an automatic ARIMA model to calculate short term forecasts based on the model used by TRAMO. Using the ARIMA model often improves estimation of the different time series components.
You may get an error if you try using ARIMA on a series that doesn’t meet the necessary conditions, such as having at least three years of history and only positive values. In this case, the report will include a description of the problem.
Note that ARIMA is always needed for the SEATS method, so this option will be automatically selected.
Trading day
This instructs the program to do an AIC-based test to check for a trading day effect, using Monday-Friday weeks. If there is a significant effect, this factor will be included in the ARIMA model.
The instruction aictest=td will be added to the regression element of the configuration passed to the X-13-ARIMA-SEATS program.
Easter
This instructs the program to do an AIC-based test to see if there is an effect of the Easter holiday. If there is a significant effect, this factor will be included in the ARIMA model.
The instruction aictest=easter will be added to the regression element of the configuration passed to the X-13-ARIMA-SEATS program.
Outlier
Included in X-13 ARIMA SEATS program, automatically checks for single point outliers and level shifts. The results can be found in Report.
Constant
You can add a trend constant regression variable by checking box in the constant column.
Conditional
When this option is selected, the seasonal adjustment will only be applied if the series is not already seasonally adjusted by the source or by using another seasonal adjustment analysis.
Output
Drop-down menu to output additional components.
Trend
This produces a series of the final trend-cycle, which is the long-term and medium-to-long term movements of the series.
Seasonal component
This feature is available in Macrobond 1.28 and later.
This produces a series whose values quantify variations in the level of the observed series that recur with the same direction and a similar magnitude at time intervals of length one year. (Length is measured in the calendar units of the observed series-- usually quarters or months, sometimes semesters, weeks, or other units.)
Irregular component
This feature is available in Macrobond 1.28 and later.
The irregular component is equal to the seasonally adjusted series divided by the trend-cycle component after removal of outlier effects.
The information about outliers and transform function can be found in Report.
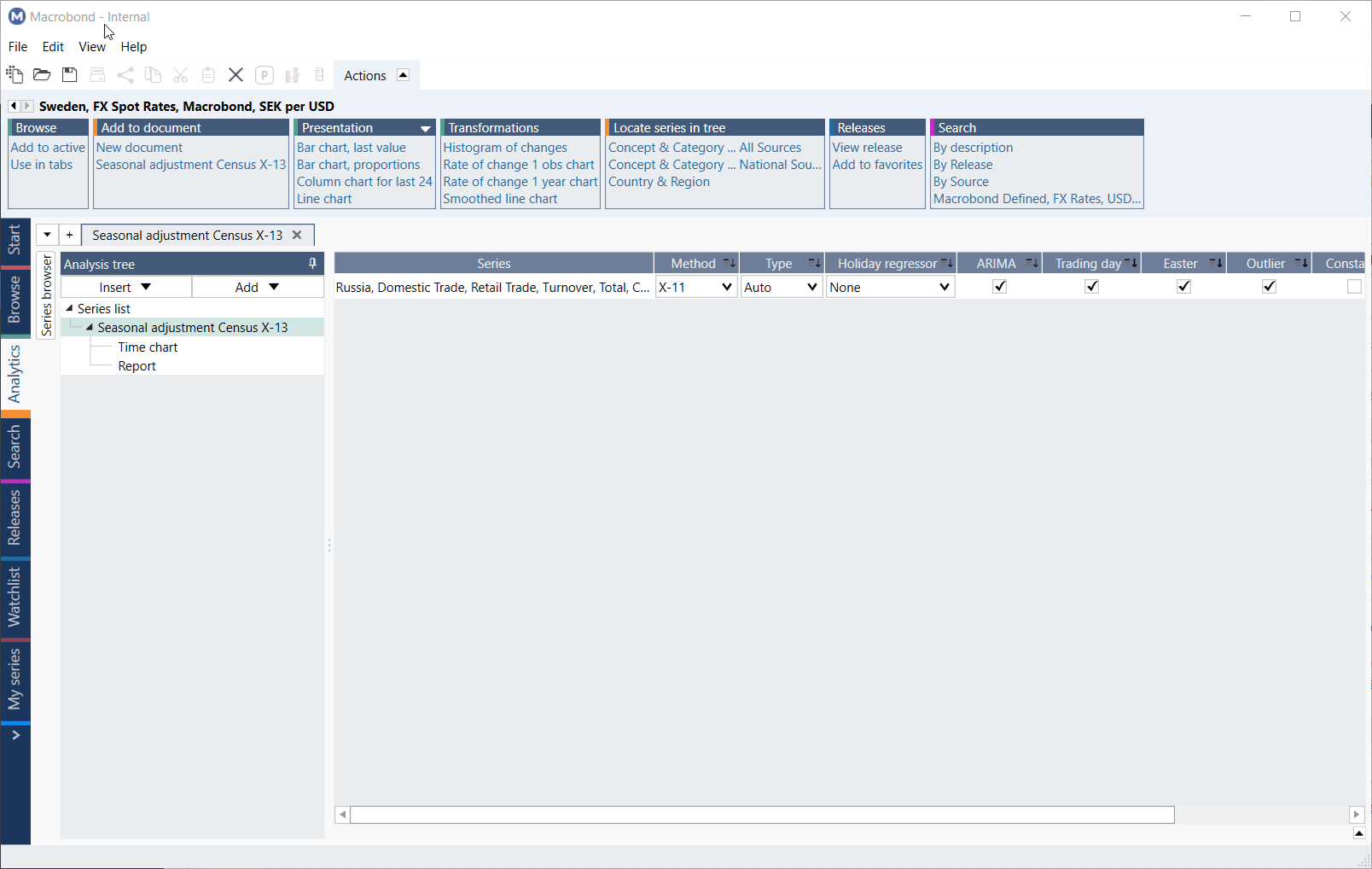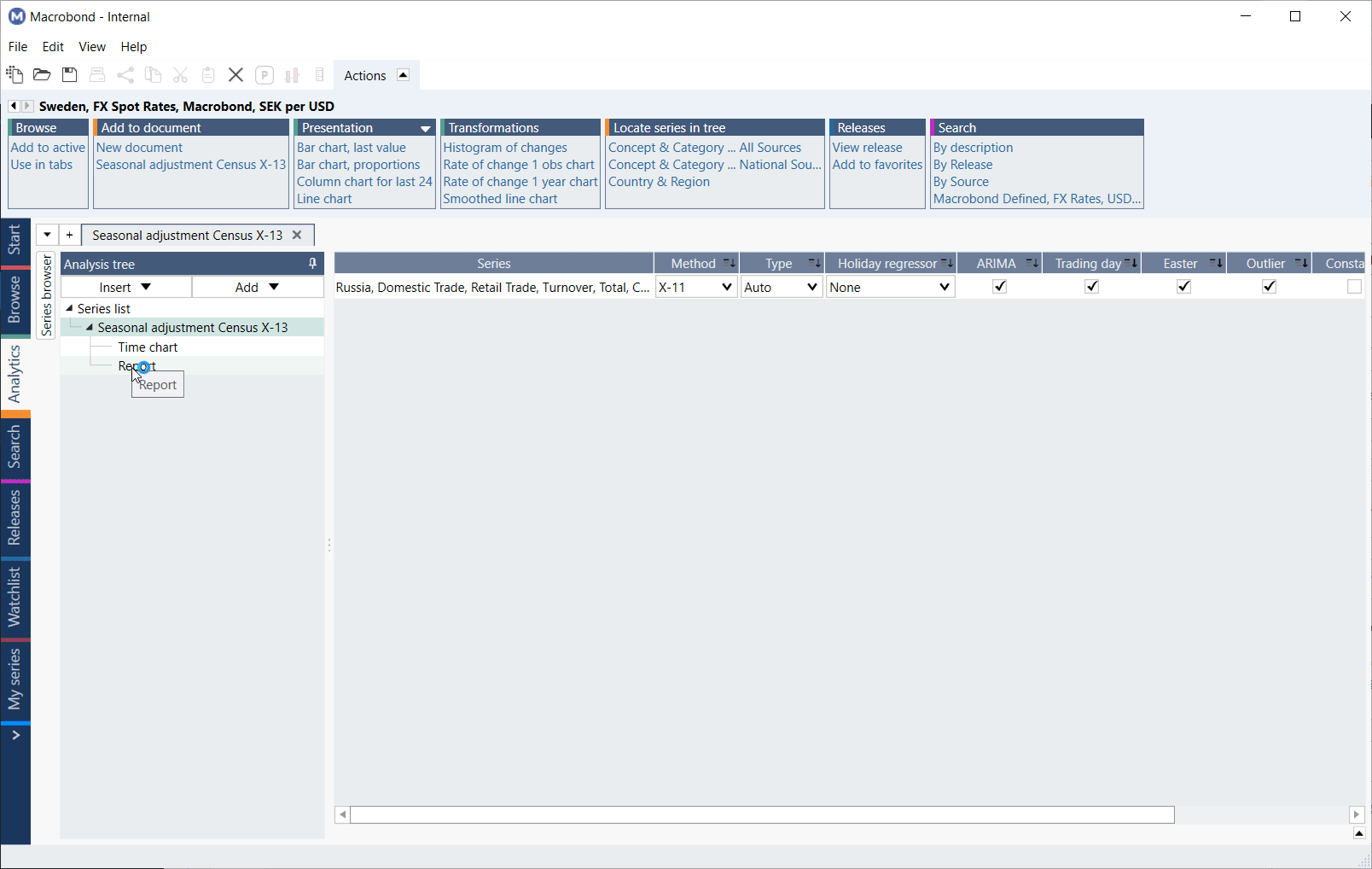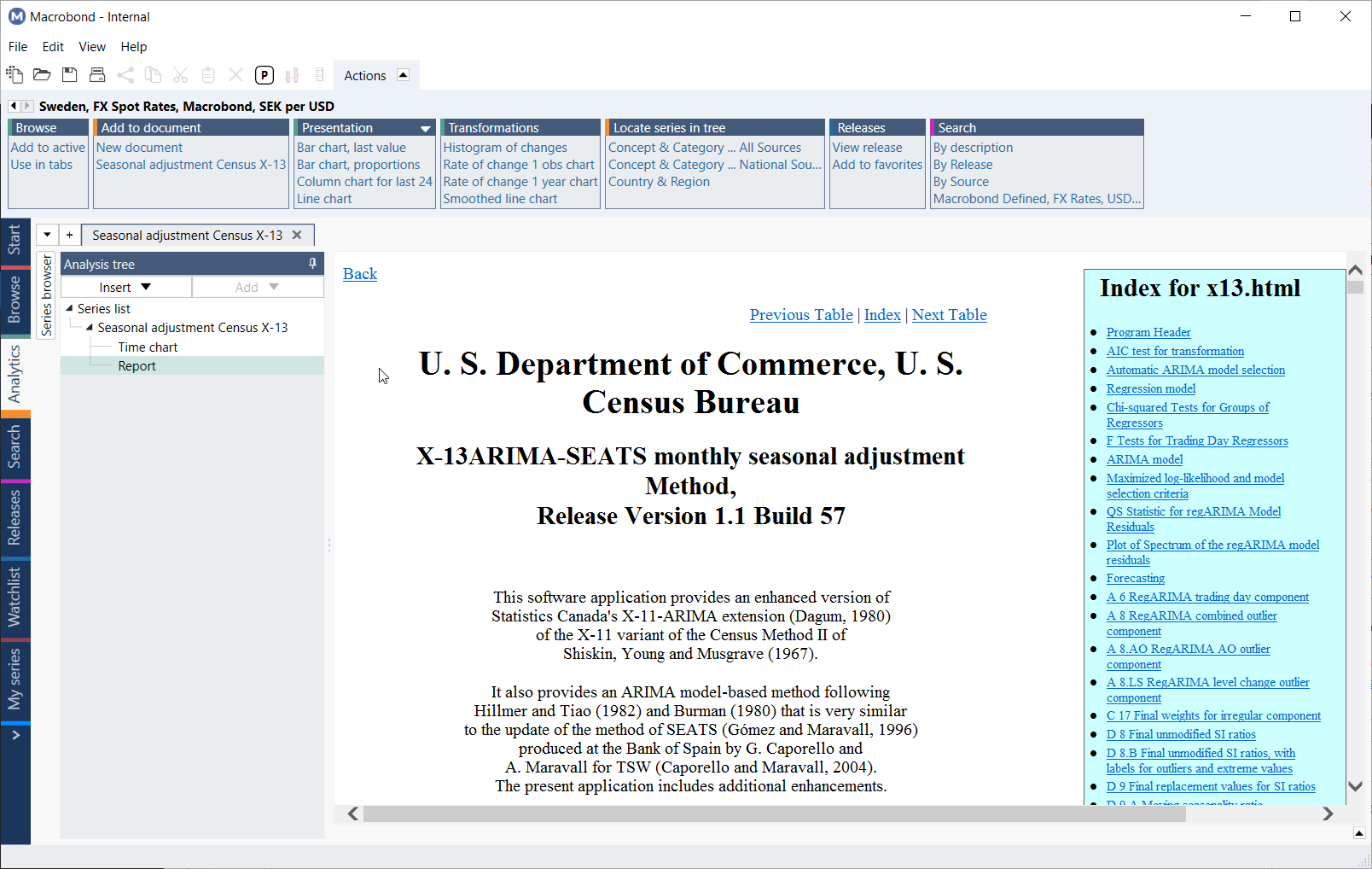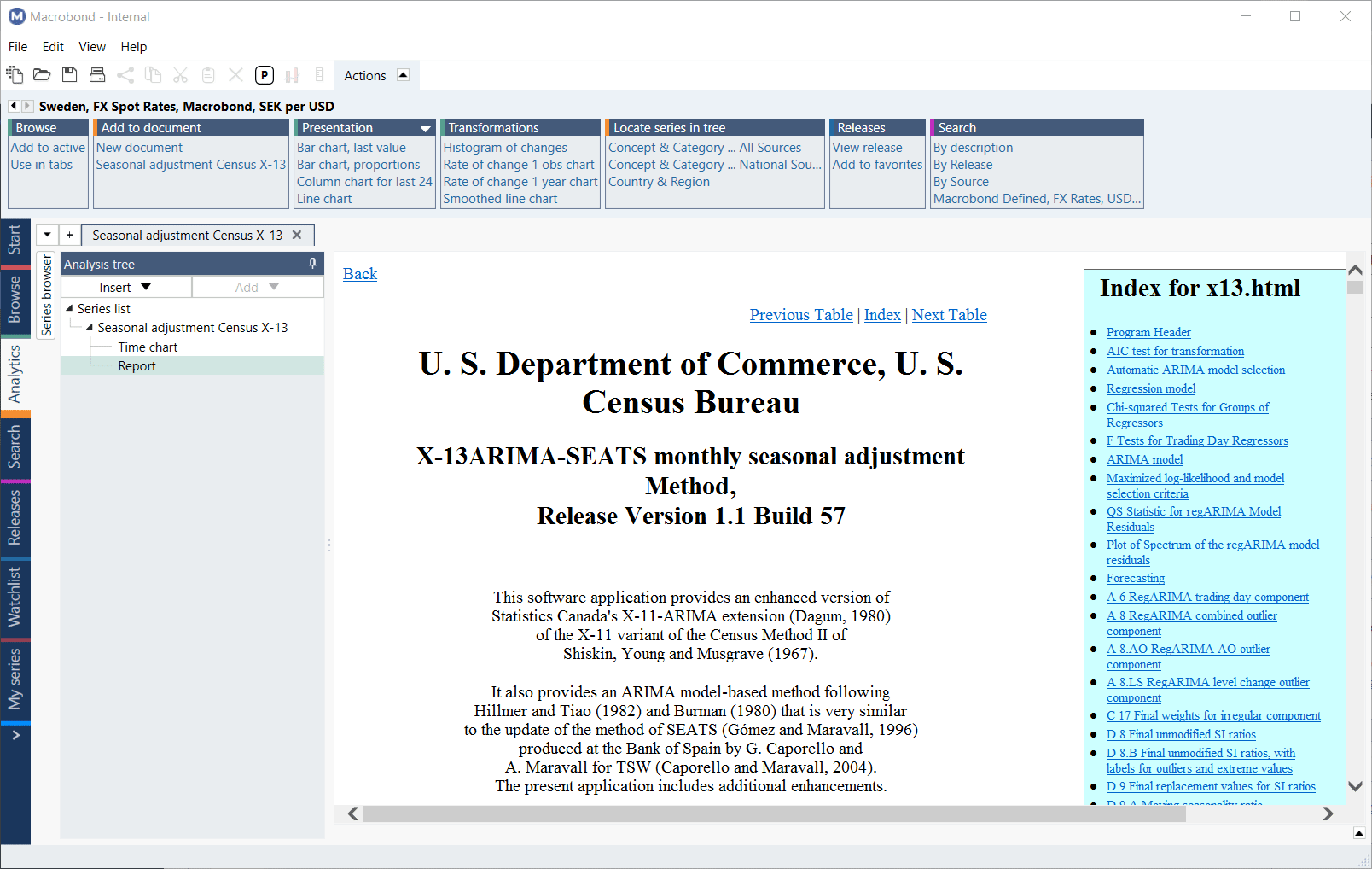
Report
A Report is available as standard output for this analysis, it includes relevant statistics and information. It is generated by Census X-13 ARIMA-SEATS program and automatically added once you select the analysis. The report will contain any errors reported by the program.
To open the report, first click on the series you're interested in. In the same window, whole report will be available:
Example
In this example we applied Seasonal adjustment Census X-13 to Russian retail trade and added the calculated trend.
Compare series with and without our Holiday regressor on series with applied SEATS method.
Compare series with and without our Holiday regressor on series with applied SEATS method..